What Is Cache?
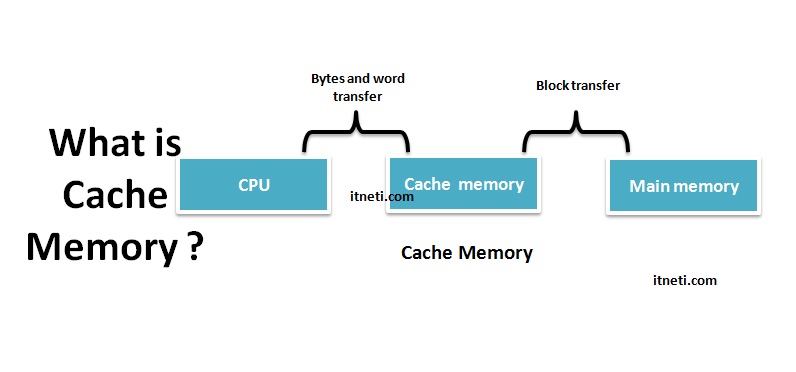
The cache memory is one of the most fastest memory . Though it is costlier than the main memory but more useful than registers. The cache memory basically acts as a buffer between the main memory and the CPU. Moreover, it synchronises with the speed of the CPU. cache memory stores the data and instructions which the CPU uses more frequently so that it does not have to access the main memory again and again and again. Therefore the average time to access the main memory decreases.It is placed between the main memory and the CPU. Moreover, for any data, the CPU first checks the cache and then the main memory.
●Caches exists in both hardware and software.
●In CPU, which processes data from the software on your systems, also has its own cache. This CPU cache is a compact memory block intended to aid the CPU in retrieving frequently accessed data. It saves information that the device’s primary memory utilises to run instructions significantly faster.
●All surfing browser have its own cache, like Microsoft Edge, Google Chrome, Firefox, and Safari. A browser cache saves files necessary for displaying web pages that the browser accesses.
How Does Cache Work?
●The data in a cache is typically stored in hardware with immediate access, like RAM (random access memory), and may be utilized in intersection with a software component. The fundamental objective of a cache is to improve data retrieval speed by eliminating the need to contact the slower storage layer behind it.
●A cache typically stores a fraction of data temporarily in exchange for capacity, as opposed to data archives, where data is often comprehensive and persistent.
●When the cache client tries to retrieve data, it checks the caching first. If the data is located in the cache, it is called a cache hit. The proportion of attempts that provide a cache hit is known as the cache hit rate or ratio.
●Data that is not located in the cache is taken from the main memory and put into the cache. This is known as a cache miss. How this is accomplished and what information is expelled from the cache to create space for new data is determined by the caching algorithms, cache mechanisms, and system regulations.
Types of cache memory:
Types of Cache Memory
There are two types, as follows:
Primary Cache
It’s located on the processor chip always. Besides, its access time is comparable to the processor.
Secondary Cache
This memory is present between the primary cache and the main memory. Besides, we can also call it level 2 (L2) cache.
Other types of cache memory
1. L1 cache memory
L1 is a register incorporated into the CPU and the most common type of cache memory. The size of the L1 cache varies between 2KB and 64KB, depending on the computer processor, which is quite modest compared to other caches. The CPU’s necessary instructions are first sought in L1 Cache. Registers include accumulators, address registers, and program counters, among many others.
2. L2 cache memory
Level 2 cache, also called the secondary cache, is frequently larger than the L1 cache. The L2 cache may be incorporated in the CPU or located in a standalone chip or coprocessor, with a high-frequency alternative system bus linking the cache and CPU. Thus, it will not be slowed down by the main bus system’s congestion.
3. L3 cache memory
Level 3 cache is a customized memory designed to increase L1 and L2 speed. L1 or L2 may be much quicker than L3, while L3 is often twice as fast as DRAM. Each core of a multicore CPU may have its own L1 and L2 cache, and they can pool an L3 cache. If such an L3 cache accesses a command, it is often promoted to a cache level higher than L3.
4. Disk cache
This form of caching produces a copy of any RAM-resident data you modify. Typically, the entire folder is saved into the cache because the computer anticipates that you may need part of the information. Therefore, accessing a file for the very first occasion may take much more time than accessing a file contained inside it.
5. Persistent cache
This cache relates to the storage space where data is preserved during a system restart or crash. Battery backups are employed to secure data, or data is transferred to a dynamic RAM with a battery backup as an additional safeguard against data loss.
6. Flash cache
The flash cache, also called solid-state drive caching, employs NAND flash memory chips (a non-volatile storage technology) to store data temporarily. Flash cache responds to data requests quicker than a typical hard disc drive or as part of the backup store.
7. Persistent cache
Persistent cache is a storing mechanism in which data is not lost upon a system restart or crash. Battery backups are employed to secure data, or data is transferred to a dynamic RAM with a battery backup as an additional safeguard against data loss.
8. Browser and app cache
Web browsers save different sections of websites, including images, JavaScript, and queries, on the hard disc. One must be able to determine how much storage space has been used by cached images if you erase your browser’s history in its settings. A cache for an application is identical to a web cache. It holds information such as codes and files in the application’s memory so that they may be accessed
Basic Operations of Cache Memory
Its basic operations are as follows:
- The CPU first checks any required data in the cache. Furthermore, it does not access the main memory if that data is present in the cache.
- On the other hand, if the data is not present in the cache then it accesses the main memory.
- The block of words that the CPU accesses currently is transferred from the main memory to the cache for quick access in the future.
- The hit ratio defines the performance of the cache memory.
Advantages of Cache Memory
The advantages are as follows:
- It is faster than the main memory.
- The access time is quite less in comparison to the main memory.
- The speed of accessing data increases hence, the CPU works faster.
- Moreover, the performance of the CPU also becomes better.
- The recent data stores in the cache and therefore, the outputs are faster.
Disadvantages of Cache Memory
The disadvantages are as follows:
- It is quite expensive.
- The storage capacity is limited.